Overview
DevShelf is a classical information retrieval system designed to demonstrate how modern search engines work beneath abstraction layers like Lucene or ElasticSearch.
It serves as the foundational counterpart to my RAG work — focusing on lexical retrieval, indexing theory, and ranking mechanics rather than language models.
DevShelf indexes and ranks Computer Science literature using offline preprocessing and deterministic scoring, prioritizing predictability, explainability, and performance.
⬇️ Download
DevShelf is distributed as a self-contained desktop application for Windows.
Windows Installer
- 64-bit installer (Windows 10 / 11)
- No external dependencies required
Latest stable release · Windows 10 / 11 · 64-bit
DevShelf is designed as a read-only search system.
All indexing is performed offline; the runtime application only performs in-memory querying.
⚙️ System Architecture
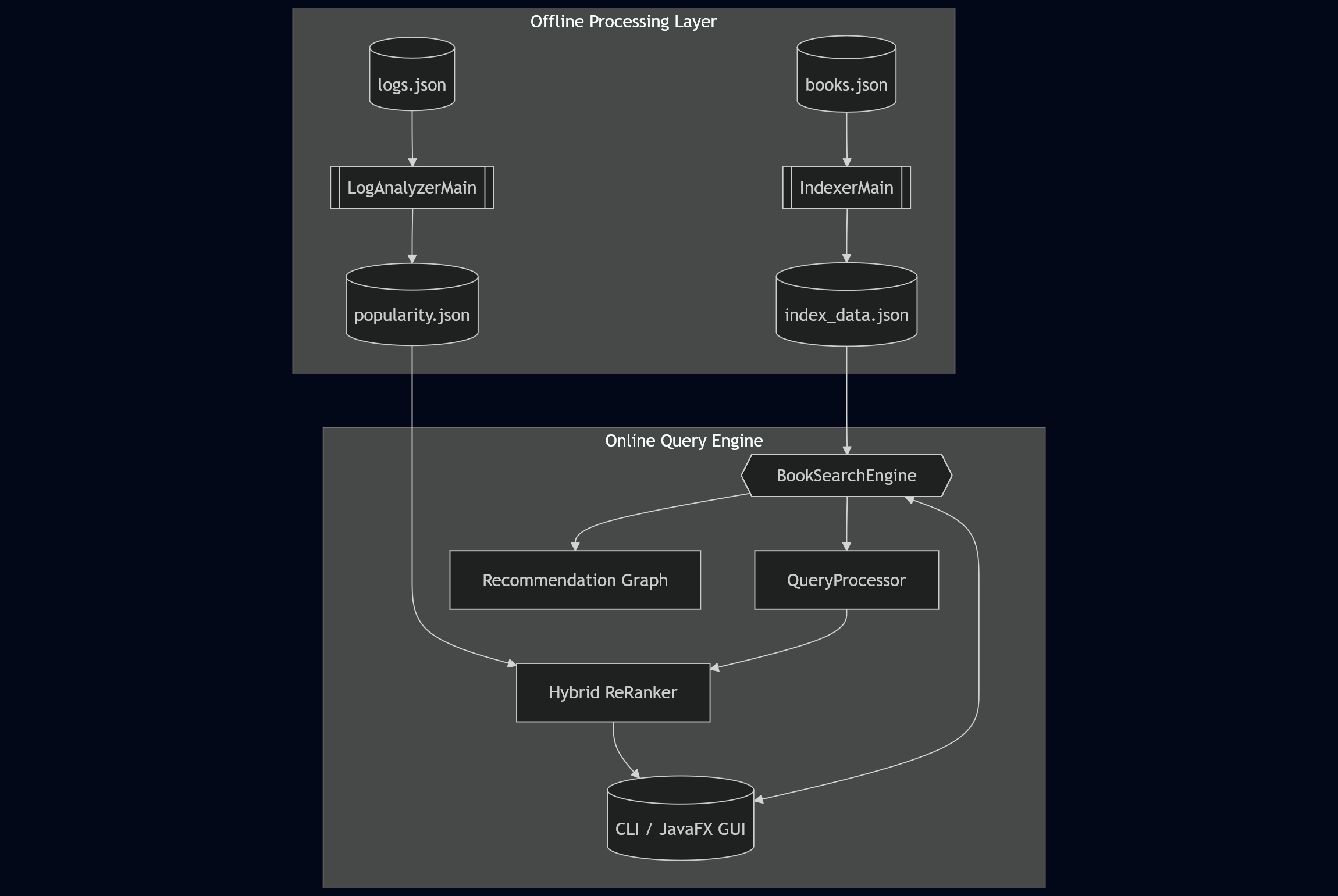
DevShelf follows a split execution model that separates heavy computation from query-time execution.
Architectural Layers
Offline Indexing Layer (
IndexerMain)- Corpus traversal
- Text normalization
- Index construction
Online Query Layer (
BookSearchEngine)- In-memory retrieval
- Sub-millisecond response times
- Deterministic ranking
This separation mirrors how real-world search engines maintain low latency at scale.
Architecture Diagram
🏗️ Offline Indexing
Index construction is treated as a batch operation to remove expensive computation from the runtime path.
Text Processing
Tokenization, stop-word removal, and stemming via a custom preprocessing pipeline.Primary Data Structure
A Positional Inverted Index, serialized for fast keyword-to-document lookup.Design Goal
Shift complexity out of the query path to guarantee predictable performance.
🔎 Query Processing
At runtime, DevShelf executes a multi-stage retrieval pipeline:
Lexical Retrieval
Candidate documents are retrieved directly from the inverted index.Fuzzy Matching
Typographical errors are handled using Levenshtein Distance–based correction.Autocomplete
Query suggestions are generated using a Trie (Prefix Tree) with O(L) lookup complexity.
🧠 Hybrid Ranking Strategy
Document relevance is computed using a weighted scoring model that blends lexical relevance with user behavior.
Conceptual Scoring Breakdown:
| Signal | Weight |
|---|---|
| TF-IDF | 0.6 |
| Popularity | 0.2 |
| User Rating | 0.2 |
This approach demonstrates how classical IR systems evolve beyond pure keyword matching.
👥 Engineering Ownership
DevShelf was built as a focused systems project with clear ownership boundaries.
| Role | Engineer | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Architect | Muhammad Qasim | Search engine design, indexing algorithms, ranking logic |
| Frontend Engineer | Nancy Chawla | JavaFX UI, application flow |
| Feature Engineer | Ritika Lund | Recommendations, filtering, sorting |
Positioning Within My Work
DevShelf represents my foundation in classical search systems:
- Inverted indices
- Vector space models
- Ranking theory
- Query optimization
These principles directly inform my work on modern Retrieval-Augmented Generation systems, where retrieval quality determines downstream LLM accuracy.
Related System
- MQNotebook — Enterprise-Grade RAG System
https://kas-sim.github.io/systems/mqnotebook/
Documentation
For detailed implementation notes, algorithms, and design rationale:
